
Exploring the Inner Workings of an Animal Cell: A Cross-Sectional View
Animal cells, the basic building blocks of all animals, are complex microscopic structures containing various specialized components. To better understand their inner workings, let's examine a cross-section of a typical animal cell.
Key Components of an Animal Cell
pen_spark
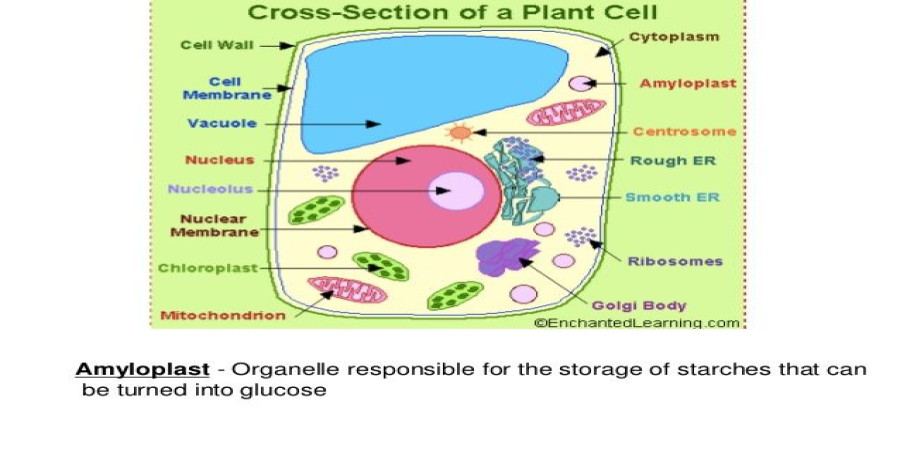
labeled crosssection of an animal cell
-
Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane): The thin, flexible outer boundary that separates the cell's internal environment from the external one. It controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
-
Cytoplasm: A gel-like fluid that fills the cell and contains organelles and other cellular structures.
-
Nucleus: The cell's control center. It houses the DNA, which contains the genetic instructions for the cell's functions.
- Nucleolus: A dense region within the nucleus where ribosomes, the cell's protein factories, are made.
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): A folded membrane network involved in protein and lipid synthesis and transport.
- Rough ER: Studded with ribosomes, involved in the synthesis of proteins that are usually exported from the cell.
- Smooth ER: No ribosomes, involved in lipid synthesis and detoxification processes.
-
Golgi Apparatus: This stack of flattened sacs modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for transport within or out of the cell.
-
Mitochondria: The cell's powerhouses. They generate ATP (energy molecules) through cellular respiration.
-
Lysosomes: Small sacs containing digestive enzymes to break down waste products and cellular debris.
-
Centrioles: Cylindrical structures that play a role in cell division.
Important Notes:
- Not all animal cells have all these components. Specialized cells may have additional or unique structures.
- The size and proportion of organelles can vary depending on the cell's function.
Understanding Animal Cells and Their Functions
By examining a cross-section, we can appreciate the intricate organization of these microscopic units of life. Each organelle plays a vital role in cellular processes such as:
- Energy production
- Protein synthesis
- Waste disposal
- Cellular division
References
- Biology LibreTexts – Animal Cell Structure
- ThoughtCo – Inside an Animal Cell
Let me know if you'd like to explore specific functions of organelles or different types of animal cells in more depth!
Popular articles

Apr 11, 2024 07:40 PM

May 25, 2024 08:09 PM

Apr 11, 2024 07:22 PM
Apr 10, 2024 07:59 PM

Mar 14, 2024 07:53 PM
Comments (0)